All about Gold
If you’ve been following Ethical Jewellery Australia (EJA) for any length of time, you’ll probably have noticed we always (and I mean always) mention that the precious metals we use in the jewellery we make for our customers – gold, platinum and palladium – are recycled in origin.
It’s not just because we’re good little recyclers and don’t like seeing things go to waste. There’s a whole lot more to it than that.
There’s gold, and then there’s gold
This year most of our customers have been preferring platinum and palladium. But when we do make a piece of gold jewellery, the gold itself comes from one of only two possible sources. Almost exclusively it’s recycled in origin, though we do offer fair trade gold as an option.
Outside our little neck of the woods however, there is another possibility. Most manufacturing jewellers use mined gold, or what might be called ‘primary gold’ (that isn’t fair trade in origin).
Let’s take a quick look at each so you can appreciate why we’ve made the choices we have.
Primary Gold
Primary gold is gold that has been dug out of the ground and is sold as an un-branded commodity.
It could just as easily have originated from an open-cut mine in Australia or have come from an illegal artisanal mine in Angola. It might also have been used to launder drug cartel money out of South America, or it might be squeaky clean. For the most part, because the supply chain is so porous, there’s no way of knowing at the consumer level*.
*The gold mining industry is taking steps to change this – with what’s being called “mine to finger” traceability, using Blockchain technology. This development however is still in its early days. Similarly, the Alliance for Responsible Mining (ARM) and RESOLVE have developed a code of conduct (called CRAFT) to facilitate the entry of small-scale mining operations into the market.
Primary gold mining tends to get broken up into two broad categories. The first is medium- to large-scale mining and the second is Artisanal Small-scale Mining (ASM). And whilst there’s no world-wide accepted definition, ASM is usually described as:
- For below-ground operations, one that processes less than 50,000 tonnes of earth per annum; or
- For above-ground operations, one that process less than 100,000 tonnes of earth per annum.
Medium- and large-scale mining is everything else – open-cut or below-ground.
Medium- and large-scale mines tend to be highly regulated and capital intensive with a relatively small labour input. ASMs range from formal (licenced) operations to informal and illegal mines. They’re mostly found in developing nations where they’re largely labour-intensive, pick and shovel type operations Often using an exploited workforce that can (and often does) incorporate child labour.
Fair-mined (or fair trade) Gold
Fair trade gold is a subset of the ASM sector that (according to Verite) produces collectively around 500kgs of traceable gold per annum. (That’s less than 0.02% of all primary production.)
As it is with most fair trade products, the primary objective of the fair-mined gold movement is to improve the lives of ASM communities by ensuring workers get paid a fair amount. Also that their working conditions are safe, that they carry out operations responsibly and child labour is eliminated. Moreover, communities with fair-mined gold certification also (typically) receive production bonuses. These can amount to several hundred thousand dollars to aid with local community development each year.
This is a worthwhile enterprise because, on the whole, ASM communities – particularly in developing nations – get a pretty raw deal. (Presently it’s estimated that 15 million people work directly in ASM with the sector indirectly supporting up to 100 million world wide.)
Workplace deaths and child labour are common, slavery and human trafficking are real, as is conflict funding and criminal corruption. Pay rates for miners are often barely subsistence. And long-term damage to the local environment and community health (particularly from mercury pollution) is endemic.
And the biggest problem is, due to a lack of economic development, most people in these communities have little if any other choice if they want to survive.
Because of the human and environmental costs of primary mining, supporters of the fair-mined gold movement argue strongly in favour of the product. And whilst we support their efforts to a degree, there is another alternative that we think is just as worthy. (Albeit for very different reasons.)
Recycled Gold
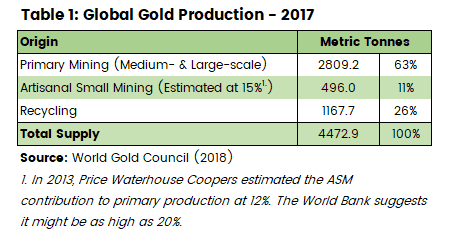
As you can see in Table 1 above, recycled gold contributed around about 26% of global production in 2017 and has sat at around 25-30% since the mid-2000s (World Gold Council – 2018).
What we like about recycled gold is its vastly smaller contribution to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions (primarily CO2) than does mining.
It’s true that recycling (re-refining) takes place almost exclusively in developed countries so it doesn’t directly benefit ASM communities, but it does benefit everyone to some degree.
Table 2 (below) shows what contribution the various gold production stages make to overall GHG (CO2equivalents) emissions. Note that the refining step – which is the only step involved in recycling – makes a considerably smaller contribution to greenhouse gas emissions than the preceding ones.
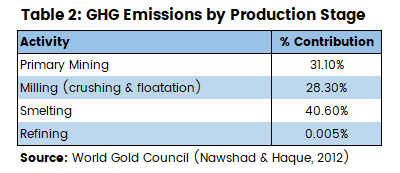
Of course, this only has some meaning if you have some context in the form of quantity of greenhouse gases.
How much CO2?
In its 2018 published report; Gold and Climate Change: An introduction, figures obtained by the World Gold Council indicate that gold production yields an estimated 38,100 tonnes of CO2e per tonne produced.
Let that sink in for a moment … that’s 38,100 tonnes of CO2e for every 1 tonne of gold produced.
(By contrast, the steel industry produces 2.3 tonnes of CO2e for every tonne of steel produced.)
Take a look at what happens when we apply that 38,100:1 ratio to the numbers in Tables 1 and 2. (Bearing in mind that recycled gold only contributes to CO2e emissions at the refining stage.)
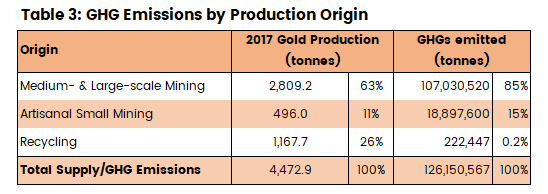
As you can see in Table 3 above, despite making up 26% of the global supply, recycling contributes less than 0.2% of greenhouse gas emissions.
Of course, 222,450 tonnes of CO2e per annum from recycling gold isn’t meaningless. Nonetheless that’s 566 times fewer GHG emissions than from mining! (On a per tonne basis, recycling gold emits approximately 190 tonnes of CO2e per tonne of gold vs 38,100 tonnes of CO2e from mining. About 200 times fewer emissions.)
This is why EJA is very much in favour of using recycled gold. Climate change affects everyone, no matter where you live.
What about ‘green-washing’?
The recycling sector has come under scrutiny in recent years because of a thing called ‘green-washing’.
This is a process by which illegally or unethically sourced gold (often from illegal artisanal small mining, from production theft and criminal money laundering operations – United Nations Inter-regional Crime and Justice Research Institute, 2016) enters the supply chain as “scrap” before the refining process to then be on-sold as ‘recycled gold’. Thus converting illegal material into ‘legal’ product.
Often quoted is the instance of a large Dubai-based refiner being caught handling untraceable gold, dealing with suppliers into conflict regions and otherwise behaving unethically. In turn this tainted the global recycled gold supply chain.
Green-washing is undoubtedly a problem, but it’s no justification for abandoning recycling. As it is with many things, it becomes a matter of choosing your suppliers carefully.
At EJA, we recycle our own waste, recycle some customer’s jewellery where appropriate and otherwise get our recycled gold from Precious Metal Technologies (PMT). PMT is a Queensland-based refiner that only uses verifiable sources of scrap gold (principally old jewellery and dental and jeweller waste). Otherwise we us Hoover & Strong, a US-based eco-refiner – again with verifiable sources of scrap.
Fair-mined gold or recycled gold – which is the ethical choice?
Promoters of fair-mined gold will tell you their product is the only ethical choice to make – their reasons being:
- Using recycled gold in jewellery has not reduced the global demand for primary gold. As such it hasn’t reduced the environmental impacts of mining. Therefore you should spend your money on fair-mined gold where it does the most good;
- The recycled gold supply chain can be tainted by green-washing, therefore can’t be trusted; and
- Recycling gold is nothing special because ‘recycling is standard practice in the jewellery industry’. So you, as a consumer, should not rank companies that promote the use of recycled gold as being any better or more environmentally responsible than anyone else.
These arguments are only partially true, and they shouldn’t be taken at face value.
The graph below shows the movements in production and demand for gold since 2010.
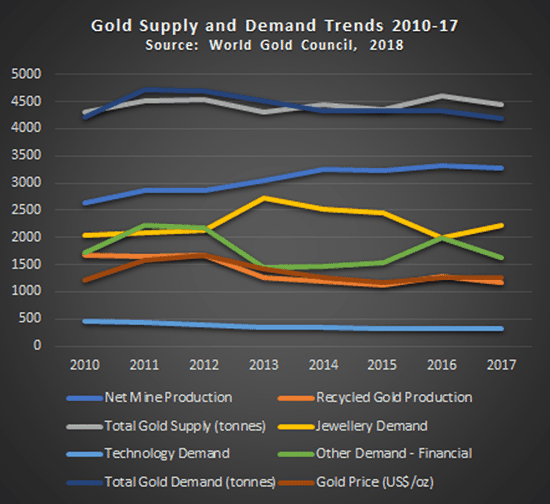
What does it reveal?:
- Demand for gold across all sectors has trended downwards since 2011 (by about 15% across the board);
- As demand for gold has decreased since 2011, so too has the price of gold decreased, down by about 25%;
- As the price of gold has dropped, the production of recycled gold has also declined (down by about 10% since 2012);
- Despite decreases in demand and price, primary gold production continues to climb – by about 1% per annum; and
- After a spike in demand for gold in jewellery in 2013, demand has since dropped by 22%.
What does this tell us?
- Despite the decrease in demand driving gold prices down, the price has yet to drop to a point where it’s uneconomic for gold mining operations to continue to grow;
- The production of recycled gold changes almost in lock-step with the price of gold, which is in turn determined by overall demand for gold; and
- Demand for gold in jewellery has not influenced primary production over the past 5 years or so.
This bears out the assertion by many commentators that recycled gold “fills the gap” between primary production and demand. (We’d speculate that it’s also probably the case that recycling is more ‘popular’ when the gold price is higher.)
So, what does all this mean for the fair-mined gold movement’s assertion that recycling has not reduced primary gold production? And from that the promise that recycling will reduce the amount of environmental damage?
‘No Dirty Gold’
Oxfam’s No Dirty Gold campaign first raised consumer’s awareness that gold mining was not doing the planet any good back in the mid-2000s. The focus was on pollution and habitat destruction.
The belief then (and reasonably so) was that if you scale up recycling, there’ll be a reduction in primary demand.
This was a rational argument but, with the benefit of hindsight, it turned out to be somewhat naïve.
The harsh reality is there would have to have been a drastic (if not catastrophic) reduction in the price of gold for mining development to slow down.
Then why bother with recycling?
If it’s true that recycled gold ‘fills the gap’ between primary production and total demand, then we would argue it has contributed significantly to moderating gold prices. Hence, it has mostly likely reduced the rate of primary mine development.
Had not recycled gold plugged the average 1,380 tonne per annum production gap between mined supply and demand, then who knows by how much gold prices would’ve increased and by how much primary production might’ve grown?
What we can say is that if that 1,380 tonnes of recycled gold were replaced by primary gold, then we’d be looking at potentially an additional 52,580,000 tonnes of CO2e being pumped into the atmosphere each year.
So, despite recycling not delivering on the hope of reducing primary production, it has most certainly contributed to significantly reducing GHG emissions.
We think that’s a good thing.
Green-washing is, in context, only a minor issue
As for the green-washing issue. Again it’s a case of suggesting we should throw the baby out with the bath water. Criminal activity by a few (that was discovered and prosecuted by the way), does not make recycling a bad thing. It just means the supply chain needs to be made more secure across the board – as is the case with all primary mining.
At EJA, we choose our suppliers very carefully to make sure the scrap they use comes from verifiable sources.
Recycling is critically important to the planet
And lastly, to suggest recycling is nothing special because ‘everyone does it’ is a misdirection. There is a big difference between recycling internally-generated waste and buying recycled raw materials.
It’s absolutely true that pretty much every jewellery manufacturer, large or small, recycles their waste precious metals. But it’s not a closed loop.
Manufacturers cannot magically produce gold (or any other precious metal) out of thin air to replace that which they sell. Every jewellery manufacturer has to buy in more gold so they can produce more jewellery. It’s where that gold comes from that counts!
In 2017, jewellery production consumed approximately 2,230 tonnes of gold. Production of recycled gold in the same year amounted to 1,168 tonnes (World Gold Council, 2018). This suggests that, at best, 52% of all gold jewellery is made with recycled gold. (We suspect that the actual figure is somewhat less than 50%. Given some recycled gold will be used in industrial and technology applications or goes into coin and investment.)
In short, using recycled gold to manufacture jewellery is not really “standard practice” as some would have you believe. In fact, it’s probably more the case that most manufacturers use a mix of whatever is the best price at the time.
Using recycled gold exclusively is most certainly not standard practice. But even if it were, it should still be applauded and valued!
Where does EJA stand?
When it comes to fair-mined or fair trade gold vs recycled gold, we don’t think it’s our business to tell you who you should or shouldn’t support. We think both have their good points, but ultimately it’s your choice.
We will make your jewellery with ethically sourced mined gold if that’s what you want. (Bearing in mind fair-mined gold is more expensive than recycled gold – for good reason.) However, recycling as our source of gold is our first preference because:
- It’s very good for the environment, and therefor benefits everyone in the long term. For that reason we’re keen to support the recycling sector and help it grow;
- It’s relatively sustainable. Gold can be recycled many times, but you can only dig it out of the ground once;
- Being ethical in the jewellery space isn’t just about supporting exploited gold miners in far flung lands. There are very many other worthy causes to consider. For example, the more than 100,000 homeless people sleeping rough every night in Australia. We think supporting local business and contributing to our local economy is a positive thing. After all, who are we to say that a human life anywhere else is more deserving than a human life in our own back yard? That’s a choice you should make for yourself; and
- There are other ways to help communities in developing nations beyond mining. It’s true that for individuals in many ASM communities, mining is their only real option in the medium-term. However, we’re inclined to support organisations (like Pact and World Vision) that also work to develop a more sustainable future in developing countries by providing education and training, health services, infrastructure and local industry and agricultural development.
Every little bit helps
EJA is not a big consumer of gold. You can count our annual usage in hundreds of grams, not thousands. So the contribution we make is small either way. (We make much more jewellery out of recycled platinum and palladium. You can read about the Platinum Group Metals supply chain here.)
Every little bit helps, but what matters most to us is that you get to make an informed choice. As we said at the outset, our first choice is locally recycled, but we’ll happily support you if your preference is fair trade gold.
Further Reading:
- The World Gold Market – 2018 (World Gold Council): www.gold.org/research/gold-market-2018
- Gold and Climate Change: An Introduction (World Gold Council, 2018): www.gold.org/download/file/6812/gold-and-climate-change-report.pdf
- Strengthening the Security and Integrity of the Precious Metals Supply Chain – United Nations Inter-regional Crime and Justice Research Institute (UNICRI), 2016: issuu.com/unicri/docs/precious_metals_report
- No Dirty Gold: earthworks.org/campaigns/no-dirty-gold/
- Code of Risk-mitigation for ASM engaging in Formal Trade (CRAFT): http://www.craftmines.org/
You might also want to read our article about choosing the right metal for your rings.
About EJA
Ethical Jewellery Australia is an online engagement and wedding ring specialist. Every ring is custom designed and made to order.
We take our customers through the whole process from design to sourcing and finally to manufacturing.
All rings are handmade in Australia with recycled metals. (We can also supply fair trade gold if requested.)
Likewise, we only every use ethically sourced diamonds and gemstones. You can choose from Argyle, recycled, vintage and lab-grown diamonds, Australian, US, Fair Trade, recycled and lab-grown coloured gemstones.
By the way, we offer an Australia-wide service.
If you would like to learn how to start your engagement ring design adventure, get in touch today.
 If you would like to learn more about designing an engagement ring, download a copy of our free 70+ page design guide.
If you would like to learn more about designing an engagement ring, download a copy of our free 70+ page design guide.
About the Author: Benn Harvey-Walker
 Benn is a Co-founder of Ethical Jewellery Australia and a keen student of ethical and sustainability issues in the jewellery world. He has a long history in sales and marketing and began working with EJA full time in early 2018.
Benn is a Co-founder of Ethical Jewellery Australia and a keen student of ethical and sustainability issues in the jewellery world. He has a long history in sales and marketing and began working with EJA full time in early 2018.
Benn co-authored the original Engagement Ring Design Guide in 2014 and edited the 2nd Edition in 2018. He is also the principal author of the wedding and commitment ring design guide.
His main responsibilities at EJA are business development and sales process management. Benn also creates technical drawings for our ring designs.


Recent Comments